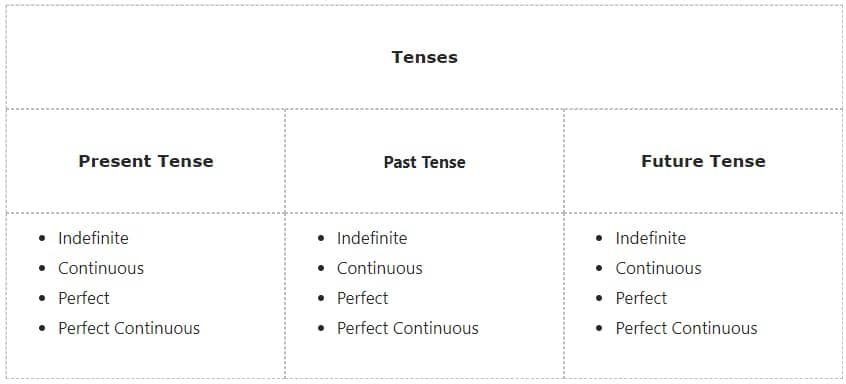
Types of tenses with example
All 12 Types of tenses with example, Tense denotes the time of action as well as the state.
12 types of Tenses with examples
- Present Indefinite
- Simple Past
- Simple future
- Present Continuous
- Past Continuous
- Future Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Past perfect
- Future Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
- Past perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect Continuous
(This is the list of 12 Types of tenses with example, See examples below)
Note: Questions are often based on confusing pairs.
Confusing Pairs of tense
- (Simple present & Present Continuous)
- (Continuous & Perfect continuous)
- (Present perfect & Simple past)
- (Simple past & Past perfect)
Present Indefinite tense
Under Present Indefinite we included the following activities:
(Routine Action)
- Regular Action: I come here daily.
- Irregular Action: Earthquake comes in Japan.
- Habits: He smokes.
- Universal Truth: The sun rises in the East.
Note: In newspaper headlines and commentary of sports, Simple present tense is used.
Examples:
- PM sings deal.
- Sachin strikes the ball and off it goes across the boundary lines.
Simple Present tense is used to express planned action of near future.
Examples: Pm leaves for China next week.
Sentence formation
(If Sub is I, we, they, you or plural)
- Positive sentence: Subject + V1 + object.
- Negative sentence: Subject + do not (don’t) + V1 + object.
- Questions:
Do + Subject + V1 + object?
Do + Subject + not + V1 + object?
Don’t + Subject + V1 + object?
If the subject is he, she, it, name or singular
- Positive sentence: Subject + V1 s/es + obj.
- Negative sentence: Subject + does not (doesn’t) + V1 + Object.
- Questions:
Does + Subject + V1 + object?
Does + Subject + not + V1 + object?
Doesn’t + Subject + V1 + object?
Consider the following sentences:
| 1. | What he knows about you? (wrong) What does he know about you? (Right) |
| 2. | I do not know what he knows about you. (Right) |
| 3. | The appeal of the victims to transfer the case related to riots to some states do not affect the merit of the case. (Change ‘do’ into ‘does’ as the main subject is ‘appeal’) |
Explanation of the above sentences.
- In the 1st statement ‘what’ is being used to ask a question. Hence interrogative form should be used after ‘what’.
- In the 2nd sentence ‘what’ is joining two sentences. Thus a normal sentence should follow ‘what’.
- A verb should always agree with the main subject of the sentence. We often relate the verb with the nearest subject but this is wrong. (Types of tenses with example)
Simple Past tense with example
(An action that is over is expressed in Simple past tense.)
Examples: I saw you but you did not see me
Sentence formation
- Positive sentence: Subject + V2 + Object
- Negative sentence: Subject + Did not (didn’t) + V1 + Object
- Questions:
Did + Subject + V1 + Object?
Did + Subject + V1 + Object?
Didn’t + Subject + V1 + Object?
Note: If the sentence starts with ‘It’s time’, ‘It’s high time’ or ‘it’s high time’, and if it is followed by a subject, the verb that will follow the subject will in second (V2) form.
Examples:
- It’s time you should study. (wrong)
- It’s time you studied. (right)
If ‘It’s time is followed by ‘to’, V1’ will be used.
Examples: It’s time to study.
Usually in a sentence, ‘do’, ‘does’ and ‘did’ is not used in a positive sentence as a helping verb. But to emphasise the main verb, we use ‘do’ ‘does’ and ‘did’ before the main verb. In such sentences, the main verb should be in the ‘V1’ form.
- You do come here everyday. (Right)
- He did make a mistake (Right)
If past time is given in a sentence, the sentence is in Simple Past Tense.
Examples:
- I have come yesterday. (wrong)
- I came yesterday. (Right)
Simple Future tense
An action to take place in future comes under Simple Future Tense.
Examples: I shall meet you tomorrow.
Sentence formation
- Positive sentence: Sub + Shall/will + V1 + obj
- Negative sentence: Sub + shall/will + not + V1 + obj
- Questions:
Shall/Will + Sub + V1 + obj?
Shall/Will + Sub + not + V1 + obj?
Shan’t/won’t + Sub + V1 + obj?
Note: Use of shall/will is explained in Modals.
Present Continuous tense
(An action that is going on at the time of speaking comes in Present Continuous Tense.)
Examples: I am studying English now.
Sometimes some events are going on even at the time of speaking but we cannot see them, they too come in (Types of tenses with example) Present Continuous Tense.
Examples:
- Coastal areas are getting submerged.
- Population is increasing day by day.
Note: For events that will take place in the near future, Present Continuous Tense is used
Examples: I am going to Mumbai tomorrow.
Sentence formation
- Positive sentence: Sub + is/am/are + V1 + ing + obj
- Negative sentence:
Sub + is/am/are + V1 + not + ing + obj
Sub + isn’t/aren’t/am not + V1 + ing + obj - Questions:
Is/am/are + Sub + not + V1 + ing + obj?
Is/am/are + Sub + not + V1 + ing + obj?
Isn’t/aren’t + Sub + not + V1 + ing + obj?
‘Am not’ has no contracted form. Hence in question tag aren’t is used.
Examples: I am fine, aren’t I?
Use of is/am/are
- Is: he/she/it/name/singular
- Am: With I
- Are: With you/we/they/all/plural
Note:
- My father is working in a bank and my brother is studying in a school. (wrong)
- My father works in a bank and my brother studies in a school. (Right)
If the statement deals with a routine action, Simple Present Tense is used and not Present Continuous Tense. But if the work is just a temporary routing action, Present Continuous Tense is used.
Examples: I am preparing for competitive exams now-a-days.
Past Continuous tense
If an action was in continuation in the past, Simple Past Tense is used
Examples: I was waiting for you.
Sentence formation
- Positive sentence: Sub + was/were + V1 + ing + obj
- Negative sentence:
Sub + was/were + not + V1 + ing + obj
Sub + wasn’t/weren’t + V1 + ing + obj - Questions: Was/Were + Sub + V1 + ing + obj?
Was/Were + Sub + not + V1 + ing + obj?
Wasn’t/weren’t + Sub + V1 + ing + obj?
Use of was and were
- Was – He/she/it/name/singular
- Were – You/we/they/plural/all
In imaginary sentence, ‘were’ is used with all subjects no matter whether it is used as a helping verb or main verb.
Examples:
- I wish, I were (main verb) a bird.
- He pretended as if he were (helping verb) sleeping.
Future Continuous tense
(An action going on in future comes under Future Continuous Tense.)
Examples: We shall be taking the examination at this time, next month.
Sentence formation
- Positive sentence: Subject + shall/will + be + V1 + ing + object
- Negative sentence:
Subject + shall/will + not + be + V1 + ing + object
Subject + shan’t/won’t + be + V1 + ing + object - Questions:
Will/Shall + Subject + be + V1 + ing + obj
Will/Shall + Subject + not + be + V1 + ing + obj
Won’t/Shan’t + Subject + be + V1 + ing + obj
Note: Some verbs do not take ‘ing’ form. Hence they cannot come in Continuous tense.
List of such verbs:
| 1. | Verbs of Perception: | See, taste, smell, her, prefer, please notice, recognize. |
| 2. | Verb of Thinking Processing: | Think, know, mean, mind, remember, suppose. |
| 3. | Verb showing possession: | Own, have, belong, comprise, possess, contain, consist. |
| 4. | Verb expressing Feeling or State of mind: | Believe, like, dislike, love, adore, want, wish, desire, hate, agree, trust, imagine. |
| 5. | Verbs in General: | Look, seem, appear, affect, resemble, cost, require, become, hope, refuse. |
Examples:
- He is owing a car. (wrong)
He owns a car. (right) - This house is belonging to me. (Wrong)
This house belongs to me (right) - I am not meaning anything wrong. (wrong)
I don’t mean anything wrong. (right) - I am seeing a man standing there. (wrong)
I see a man standing there. (right)
Note: If ‘have’ denotes possession, it is not used in ‘ing’ form but if ‘have’ is denotes ‘to have fun or to eat’, ‘have’ can be used in ‘ing’ form.
Examples:
- I am having a piece of cake. (right)
I am having a car. (wrong) - I have a car. (right)
If think, remember, feel, look, appear, etc. are used to express emotions or the verbs given above are used in a progressive state, they can come in ‘ing’ form. (Types of tenses with example)
Examples:
- I am thinking you are right. (wrong)
I think you are right. (right) - I am thinking of you. (right)
It was appearing as if they were going to kill us. (wrong)
I appeared as if they were going to kill us. (right) - You are looking good. (right)
- Look! He is smelling the rose. (right)
In ‘Gerund’ & ‘Present Participle’, verbs are used in ‘ing’ form.
Examples:
- Being ill, I could not come.
- Getting a job is easy now-a-days.
- Seeing is believing.
- Swimming is good exercise.
If we use a verb after a preposition, the verb will be in ‘ing’ form.
Examples:
- Bats are capable of hearing (V1 ing) ultrasonic waves.
- We must keep away from smoking (V1 ing).
Present Perfect tense
An action that has recently finished is expressed in the Present Perfect Tense.
Examples: He has come to Delhi recently.
If the action is important and not the time of action, and the time of action is not given, we use Present Perfect Tense.
Examples:
- We have progressed a lot.
- We have reached the moon.
Sentence formation Formula chart
- Positive sentence: Subject + has/have + V3 object
- Negative sentence:
Subject + has/have + not + V3 object
Subject + hasn’t/haven’t + V3 object - Questions:
Has/ have + Subject + V3 + object?
Has/have + Subject + not + V3 + object?
Hasn’t/haven’t + Subject + V3 + object?
Use of Has/Have
- Has–With: He/She/It/Name/Singular
- Have–With: I/We/They / You / Plural / All
See the difference:
- Science has given us many new inventions. (Right)
- We have reached the moon. (Right)
- Science has given us many new inventions in the 19th century. (wrong)
- We have reached the moon on 22nd Oct. 2008. (wrong)
If past time is given, use Simple Past Tense and not Present Perfect Tense.
The correct sentences will be:
- Science gave us many life-saving drugs in the 19th century. (Right)
- We reached the moon on 22nd Oct, (Right)
Note: In the sentence, any form of ‘have’ can be followed by ‘had’ (Here ‘had’ will be the main verb). This is because, in Perfect Tense, such combinations are used.
- I have had enough problems here (Right)
- He has had his breakfast. (Right)
‘Usually’, ‘recently’, ‘already’, ‘yet’, ‘so far’ are used in Perfect Tense. ‘Yet’ is generally used in negative sentences of Present perfect.
Examples:
- He has not reached home yet (present perfect)
- He had not done any work so far. (past perfect)
If ‘since’ is followed by ‘Simple Past Tense’, ‘since’ is preceded by ‘Present Perfect Tense’.
Examples: I haven’t seen him since he left India.
Note: In such sentences, the perfect form of any modal can also be used.
Examples: He may have grown old since she last saw hi,
If since is used at the beginning of a sentence, the formation of the sentence will be as follows.-
Examples: Since he joined the army, he has not taken any leave.
Past Perfect tense
Look at the sentences given below:
- I saw him before he stopped his car. (wrong)
I had seen him before he stopped his car. (Right) - Before he understood anything the robber fled. (wrong)
Before he understood anything the robber had fled. (Right) - I met him after I finished my work. (wrong)
I met him after I had finished my work. (Right) - By the time I reached the theatre, the show started (wrong)
By the time I reached the theatre the show had started. (Right) - When Anand reached his village, he found that the news about him had preceded him. (Right)
If two actions take place in the past, one after the other, the 1st action will be in Past Perfect Tense and the 2nd action will be in Simple Past Tense, (Types of tenses with example).
Sentence formation
- Positive sentence: Subject + Had + V3 + object
- Negative sentence: Subject + Had + not + V3 + object
- Questions:
Had + Subject + V3 + object
Had + Subject + not + V3 + object
Hadn’t + Subject + V3 + object
Note: See the 5th sentence.
When Anand reached his village, he found that the news about him had preceded him.
Explanation: ‘Precede’ means ‘to come before’. The 1st action is ‘the coming of the news’ which must be in Past Perfect Tense and the 2nd action is ‘And going to the village’ which must be in Simple Past Tense.
Future Perfect tense with example
(Definition: An action that will have been completed in the future, comes under Future Perfect Tense.)
Examples: You will have finished your syllabus by the end of next month.
Look at the following sentences:
Examples:
- By the time I reach the station, the train will have left.
- By the time, Simple Present, Future Perfect
Sentence formation
- Positive sentence: Subject + will/shall + have + V3 + obj
- Negative sentence:
Subject + will/shall + not + have + V3 + obj
Subject + won’t/shan’t + have + V3 + obj - Questions:
Will/shall + sub + have + V3 + Obj?
Will/shall + sub + not + have + V3 + Obj?
Won’t/shan’t + sub + have + V3 + Obj?
Look at the difference:
- By the time I reach the station, The train will have left.
- By the time I reached the station, the train had left.
Present Perfect Continuous tense
(An action already started and still going on comes under Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
Examples: I have been living in Delhi for five years.
Sentence formation
- Positive sentence: Sub + has/have + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/since + time.
- Negative sentence:
Sub + has/have + not + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/since + time.
Sub + hasn’t/haven’t + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/since + time. - Questions:
Has/have + Sub + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/since + time.?
Has/have + Sub + not + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/since + time.?
Hasn’t/haven’t + Sub + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/since + time.?
Examples:
- I am teaching you since an hour. (wrong)
- I have been teaching you for an hour. (right)
Is used for a period of time.
Examples:
| 1. | For two hours, for the last 2 years. |
| 2. | For five years, for the last 2 months. |
| 3. | For 10 years, for the last 3 weeks. |
Since: is used for a point of time.
Examples:
| 1. | Since Monday, since the beginning. |
| 3. | Since 2008, since time immemorial. |
| 4. | Since 7 pm, since last year. |
Types of tenses with example
Past Perfect Continuous tense with example
(An activity that started in the past, continued and finished in past comes under Past perfect Continuous.)
Examples: I had been waiting for you since morning.
Sentence formation formula
- Positive sentence: Sub + had + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/since + time.
- Negative sentence: Sub + had + not + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/since + time.
- Questions:
Had + Sub + not + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/since + time ?
Had + sub + not + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/since + time ?
Hadn’t + sub + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/since + time ?
Future Perfect Continuous tense
An action that continues upto some future point of time comes under Future Perfect Continuous.
Examples: I shall have been living in Delhi for five years by the end of this year.
Sentence formation
- Positive sentence: Sub + Shall/will + have + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/from + time.
- Negative sentence:
Sub + Shall/will + not + have + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/from + time.
Sub + Shan’t/won’t + have + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/from + time. - Questions:
Shall/will + sub + not + have + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/from + time
Shall/will + sub + not + have + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/from + time
Shan’t/won’t l + sub + not + have + been + V1 + ing + obj + for/from + time
Note: Verbs that are not used in ‘ing’ form are not used in ‘continuous/perfect continuous tense’.
Such verbs should be used in Indefinite Tense instead of Continuous Tense.
For Example:
I am knowing you. (wrong)
I know you (Right)
Such verbs should be used in Perfect Tense instead of Perfect continuous tense.
For Example:
I have been knowing him for five years. (wrong)
I have known him for five years. (right)
For/since is used in both Perfect & Perfect Continuous Tense.
Examples:
- I have been living in Delhi for five years. (Right )
- I had known him for two years. (right)
If ‘for/since + time’ is used in a sentence, the sentence will be in Perfect or Perfect Continuous Tense.
Examples:
I ate nothing since morning. (Wrong)
I have eaten nothing since morning. (right)

Nice helpfull