English Grammar Non-Finite for Class 8
Hello readers, Welcome back to Performdigi, In this article, we are going to discuss English grammar Non-Finite for class 8, We have provided worksheets, exercises with answers. If you go through this article completely and complete the worksheet, you will get a basic understanding of English Non-Finite. Let’s dive in without any further ado.
Some verbs change their form at times based on that understanding we divided verbs into two types:
- Finite
- Non-finite
1. What is FINITE?
Finite verbs are those verbs that are bounded by number, person, and tense. They improve their form in agreement to the tense, verb, and subject of the verb.
Here, now will study English Grammar non-finite for class 8 in detail.
2. What are non-finite for class 8?
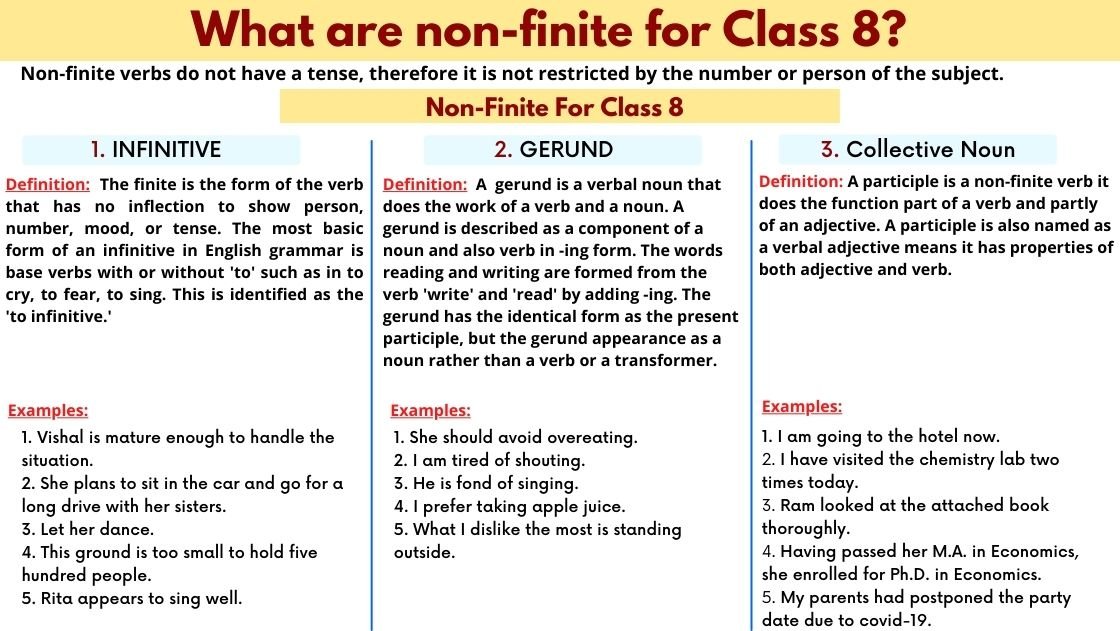
Non-finite verbs do not have a tense, therefore it is not restricted by the number or person of the subject. The three kinds of non-finite verbs are:
- INFINITIVE
- GERUND
- PARTICIPLE
1. INFINITIVE
The finite is the form of the verb that has no inflection to show person, number, mood, or tense. The most basic form of an infinitive in English grammar is base verbs with or without ‘to‘ such as in to cry, to fear, to sing. This is identified as the ‘to infinitive.‘
The infinitive is sub-divided into two kinds;
⇒ Bare Infinitive:- It is also called infinitive without ‘to‘ or plain infinitive. The bare infinitive is used with verbs like hear, bid, let, need, dare, see, make.
⇒ Infinitive Participle:- infinitives that carry ‘to‘ are called an infinitive participle
Rules for Infinitive
- Used in active voice take infinitive without to; make, know, feel, behold, notice, watch, hear, see.
- “Sooner than, would rather, had better, would sooner, rather than, had sooner.” Use bare infinitive after the following words.
- The bare infinitive is practiced after the conjunction ‘than‘
- After the modal auxiliaries infinitive such as will, shall, should, would, may, can, might, must come without ‘to‘
- Infinitive after ‘too‘
- …+ too + adjective + infinitive
- …+ too + adjective +a + noun + infinitive
- …+ too + adverb + infinitive
- If two infinitive is joined by and, the second infinitive’s ‘to‘ is usually drooped.
- so……as + infinitive
- ‘but‘ and ‘except‘ take the bare infinitive when they follow do + nothing/anything/everything.
- have/had/has + noun/pronoun followed by a bare infinitive.
- Infinitive after enough
- …+ adjective + enough + infinitive
- …+ adverb + enough + infintive
- In positive sentences, the infinitive is (with to) is used after the verb dare and need.
Examples of infinitive for class 8
- Vishal is mature enough to handle the situation.
- She plans to sit in the car and go for a long drive with her sisters.
- Let her dance.
- This ground is too small to hold five hundred people.
- Rita appears to sing well.
2. GERUND
A gerund is a verbal noun that does the work of a verb and a noun. A gerund is described as a component of a noun and also verb in –ing form. The words reading and writing are formed from the verb ‘write‘ and ‘read‘ by adding –ing. The gerund has the identical form as the present participle, but the gerund appearance as a noun rather than a verb or a transformer.
Specific Rules of Gerund
- Some verbs followed by preposition/adverb take the gerund. The most common are; care for, be against/for, give up, keep on, leave off, look forward to, put off, see about, take to, etc.
- Pardon, forgive, excuse, and prevent are not followed directed by the gerund. These take either possessive adjective/pronoun + preposition + gerund or pronouns + preposition + gerund.
- A proposition is always followed by a gerund, not by an infinitive. This is a good precept that has no objections. If we require to practice a verb subsequent to a proposition it is necessary to be a gerund. It is difficult to adopt an infinitive next to a preposition.
- The term ‘to‘ often confuses. It is either a component of an infinitive or a preposition. When ‘to‘ is supported by a noun/pronoun or gerund it is a preposition. When applied as a preposition it is constantly supported by a gerund.
- Verb + Possessive adjective/pronoun object is accompanied by a gerund and this gerund refers to the person expresses by the possessive adjective or pronoun.
Examples of gerund for class 8
- She should avoid overeating.
- I am tired of shouting.
- He is fond of singing.
- I prefer taking apple juice.
- What I dislike the most is standing outside.
3. THE PARTICIPLE
A participle is a non–finite verb it does the function part of a verb and partly of an adjective. A participle is also named as a verbal adjective means it has properties of both adjective and verb.
There are three sorts of participles;
- Present Participle (verb + ing)
- Past Participle (verb + ed)
- Perfect Participle (verb + ed/-en)
The Present Participles: Present participle is ending with -ing like seeing, singing, interesting, etc. Present participles show an unfinished action or state (which is going on).
Rules of Present Participle
- transforming a noun as an adjective.
- forming participle form.
- forming clause.
- it can substitute since/as/because + subject + verb.
- adjusting a verb, like an adverb.
The Past Participles: Past participle indicates an entire action (no longer in progress). The third form of a verb is termed a past participle. The past participle is utilized as an adjective is passive if the verb from which it is acquired is transitive. Normally, it ends in -d, -ed, -t, -n -en, or any other third form of the verb.
Rules for Participle
- forming the perfect tense form
- it can replace passive verbs
- modifying noun
- the past participle is used in the passive voice
The Perfect Participles: Perfect participle is formed by adding ‘having‘ or ‘having been‘ or ‘being‘ to the past participle form of the verb. Perfect participle signifies an action that was complete at something in the past.
Rules of Perfect Participles
- it is used when the first action covered a period of time.
- it is utilized when there is an interlude of time between the two actions.
- It is utilized to join two sentences when one action is accompanied by another with the same objective.
Examples of Participles for class 8
- I am going to the hotel now.
- I have visited the chemistry lab two times today.
- Ram looked at the attached book thoroughly.
- Having passed her M.A. in Economics, she enrolled for Ph.D. in Economics.
- My parents had postponed the party date due to covid-19.
Worksheet/Exercise Of Infinite or Non-Infinite Verb For class 8
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of non-finite verbs.
1. Playing is easier than____(to reading/reading)
2. Try____(avoiding/to avoid) being late for coaching.
3. The class needs proper____(having cleaning/cleaning)
4. The medical students refused____(changing/to change) the biology teacher.
5. Most of the boys like___(playing/have played) cricket.
6. Some girls like____(to watch/watch) the TV.
7. She wears a ___(worrying/worried) look today.
8. ____ (failed/having failed) many times in 10th, he doesn’t want to try again.
9. She is fond of ____. (cooking/having cooking)
10. Her talk left me___. (thinking/to think)
Answers:
- reading
- to avoid
- cleaning
- to change
- playing
- to watch
- worried
- having failed
- cooking
- thinking
If you want to download a pdf of English Grammar non-finite for class 8 click On the link given below.
Download pdf (1271 downloads )Summary
thank you for neat explanation.
Thanks for visit our site,
If you want to know more about “English Grammar” Non-Finite for Class 8. For any query about this topic comment below.